Total Quality Management (TQM) is a manufacturing philosophy and a structured approach that focuses on continuously improving the quality of products, processes, and services within an organization by eliminating errors in manufacturing. Rather than focusing on specific, small levels of problems within a product or organization, TQM’s methodology focuses on broader, organization-wide management that opens imperative solutions with continuous improvement. This methodology involves the improvement in various aspects of a business – From products, services, employees, and management, including all parties involved in the process of producing a product to customer satisfaction.
In this article, we will talk about what Total Quality Management is, its principles, other business improvement methodologies and how it can improve your business process.
Understanding the Principles of Total Quality Management (TQM)
Total Quality Management is a customer-centric, philosophy and management framework aimed at continuously improving the quality of products, services, and processes within an organization. It’s not just a set of tools or a one-time initiative; instead, it’s a long-term commitment to excellence that involves every level of an organization.
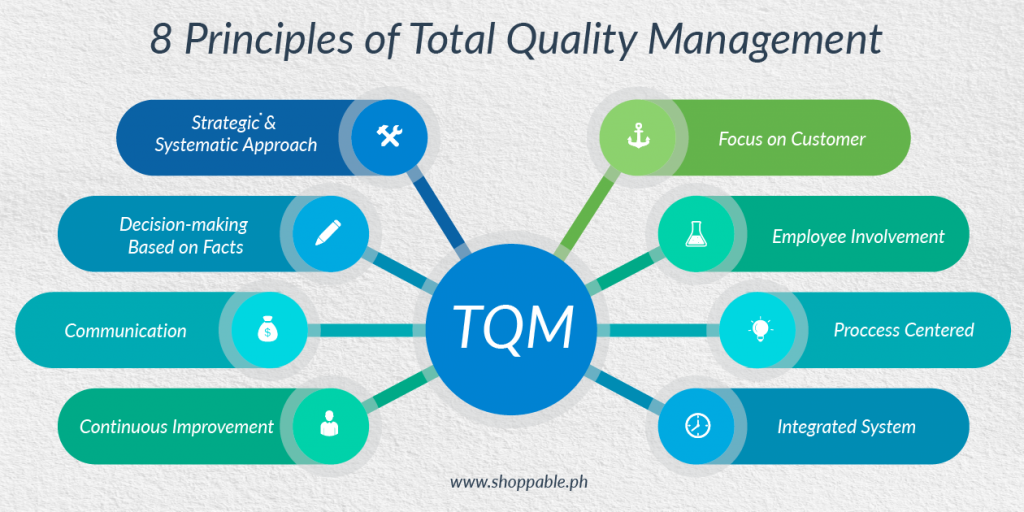
While there are no specific methodologies and principles to be followed in Total Quality Management, here are the primary principles that make Total Quality Management.
- Customer Focus
The ultimate goal of TQM is to meet or exceed customer expectations. This principle emphasizes the importance of understanding customer needs and preferences and aligning all processes and activities with the goal of enhancing customer satisfaction.
By actively seeking to understand the evolving needs, preferences, and demands of customers, organizations practicing TQM not only forge strong, lasting customer relationships but also position themselves at the front of industry excellence.
- Leadership
Effective leadership in TQM involves setting a clear direction for the organization’s quality improvement efforts. This means defining the organization’s quality objectives, goals, and strategies. Leaders articulate the importance of quality and ensure that these objectives align with the overall mission and vision of the organization.
- Employee Involvement
In the principles of Total Quality Management, the feedback of employees at every tier of an organization are not merely encouraged but cherished as invaluable assets. Team members are empowered and entrusted with active participation in the process improvement journey.
Effective leadership in TQM is about more than just overseeing quality initiatives; it’s about inspiring a culture of quality throughout the organization. Leaders provide direction, support, and a vision for quality, and they actively engage with employees to ensure that TQM principles are integrated into the fabric of the organization. When leadership is committed to TQM, it sets the stage for lasting and meaningful improvements in quality and performance.
- Process Approach
Integral to TQM’s methodology is the meticulous, refinement of processes. This entails a deep dive into operations, seeking to streamline, standardize, and optimize processes to ensure they are not only efficient but also highly effective.
TQM recognizes that high-quality outcomes are born from well-designed, well-executed processes. As a result, organizations adhering to this philosophy commit to an unceasing pursuit of process excellence, ensuring that each step is finely tuned to deliver superior results consistently.
- Continuous Improvement
The core of the TQM principles lies deeply in the culture of continuous improvement. The principles entail a systematic and ongoing evaluation of processes, where inefficiencies, bottlenecks, and errors are systematically identified and meticulously addressed. This methodology of perfection transforms organizations into dynamic, adaptable entities, pursuing the evolution to meet the challenges of an ever changing industry.
- Evidence-Based Decision Making
Fundamental to the success of TQM is the reliance on precise data and performance metrics to provide valuable insights to improvement. The principles of TQM drives an evidence-based approach to decision-making, where data analysis serves as the compass guiding organizations toward their objectives.
By collectively utilizing the power of data, organizations can pinpoint areas that need improvement, implement targeted solutions, and monitor progress with precision, eventually achieving maximum optimization and improvement.
- Systematic Approach to Management
TQM advocates for a systematic and integrated approach to managing quality across all areas of an organization. It encourages the use of quality management systems and tools.
- Communication
Effective communication is a cornerstone of Total Quality Management (TQM). This principle underscores the importance of clear, open, and transparent communication within an organization. It involves the seamless exchange of information, ideas, and feedback among all stakeholders, including employees, management, customers, and suppliers.
How Can TQM Improve Business Processes?
Enhanced Quality
The primary goal of TQM is to improve product and service quality. By implementing TQM principles, organizations can reduce defects, errors, and customer complaints, resulting in products and services that meet or exceed customer expectations.
Increased Efficiency
TQM emphasizes process optimization. By streamlining processes, eliminating waste, and reducing variability, organizations can achieve higher levels of efficiency, which can lead to cost savings and improved resource allocation.
Employee Engagement
TQM recognizes that employees are a valuable source of knowledge and innovation. Involving employees in process improvement not only leads to better solutions but also increases their job satisfaction and commitment to the organization.
Better Decision Making
TQM relies on data analysis to drive improvements. This data-driven approach helps organizations make informed decisions and prioritize initiatives that have the most significant impact on quality and performance.
Consistency
TQM promotes standardization of processes and procedures. This ensures that the same high-quality results are consistently achieved, reducing variability and increasing customer trust.
Customer Satisfaction
By aligning processes with customer needs and preferences, TQM can significantly enhance customer satisfaction and loyalty, leading to repeat business and positive word-of-mouth marketing.
Competitive Advantage
Organizations that embrace TQM often gain a competitive edge in the market. Their ability to consistently deliver high-quality products and services sets them apart from competitors and attracts more customers.
Total Management Quality vs PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) Cycle
Total Quality Management (TQM) and the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) Cycle are both methodologies aimed at achieving continuous improvement, but they have different approaches and scopes.
Key Points of TQM
Customer Focus
TQM prioritizes understanding and meeting customer needs and expectations, with the aim of delivering superior products and services.
Employee Involvement
TQM encourages employees at all levels to participate in quality improvement initiatives, fostering a sense of ownership and empowerment.
Process Optimization
TQM involves analyzing and optimizing processes to eliminate waste, reduce defects, and improve efficiency.
Key Steps of PDCA Cycle
The PDCA Cycle, also known as the Deming Cycle or Shewhart Cycle, is a systematic four-step method for continuous improvement. It is a component of TQM but focuses specifically on process improvement.
Plan
Identify a problem or opportunity for improvement, set objectives, and plan the actions needed to achieve the desired results.
Do
Execute the plan by implementing the proposed changes or improvements.
Check
Evaluate the results and compare them to the objectives. This step involves data analysis and performance measurement.
Act
Based on the evaluation, make necessary adjustments or corrections to the process. If the objectives are met, standardize the new process.
Total Quality Management (TQM) vs Six Sigma
Total Quality Management (TQM) and Six Sigma are two methodologies that aim to enhance quality and efficiency within organizations, but they differ in their focus and tools.
TQM (Total Quality Management)
As mentioned earlier, TQM is a holistic approach that emphasizes the involvement of all employees in quality improvement efforts. It prioritizes customer satisfaction, process optimization, and creating a culture of continuous improvement.
Key Points of Six Sigma
Data-Driven
Six Sigma relies heavily on statistical analysis and measurement to identify and eliminate variations in processes.
DMAIC Approach
The Six Sigma methodology follows a five-step approach: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, to systematically improve processes.
Project-Based
Six Sigma often involves dedicated project teams working on specific process improvement projects.
TQM is a broader philosophy that encompasses various principles and encourages a cultural shift toward quality, whereas Six Sigma is a highly structured, data-driven methodology focused on reducing defects and variations in processes.
Conclusion
Total Quality Management is not a quick fix; it’s a long-term commitment to excellence. When properly implemented, TQM can lead to significant improvements in product and service quality, reduced costs, higher employee morale, and enhanced customer satisfaction. By embracing the principles of TQM and continuously striving for improvement, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in today’s competitive landscape.